Erectile dysfunction (ED), commonly referred to as impotence, is a prevalent condition that affects men worldwide. Defined as the inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for satisfactory sexual performance, ED can have profound psychological and emotional impacts.
This blog will help you learn the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and lifestyle considerations associated with ED.
The Physiology of an Erection
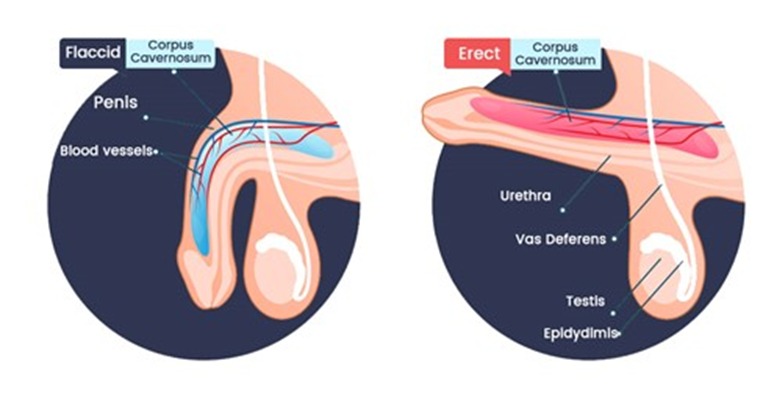
To understand erectile dysfunction, it’s essential to first grasp how a normal erection occurs. The process is a complex interaction between the nervous system, blood vessels, muscles, and psychological factors.
- Initiation: Sexual arousal, whether physical or psychological, triggers signals from the brain.
- Neurotransmitter Release: These signals cause the release of neurotransmitters from the nerve endings in the penis.
- Blood Flow Increase: The neurotransmitters cause the relaxation of smooth muscles in the corpora cavernosa, the sponge-like regions of erectile tissue. This relaxation allows blood to flow into the penis.
- Erection Maintenance: The influx of blood causes the penis to expand and become rigid. The veins that drain blood from the penis are compressed, maintaining the erection.
- Detumescence: After ejaculation or cessation of sexual arousal, the blood flows out, and the penis returns to its flaccid state.
Causes of Erectile Dysfunction
ED can result from a variety of physical and psychological factors. It’s often multifactorial, involving a combination of these elements.
Physical Causes
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Conditions such as atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) can impede blood flow to the penis, making it difficult to achieve an erection.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and nerves, essential components in achieving an erection.
- Neurological Disorders: Diseases like Parkinson’s, multiple sclerosis, and spinal cord injuries can interfere with nerve signals between the brain and the penis.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Low levels of testosterone or other hormonal disorders can affect libido and erectile function.
- Chronic Kidney Disease: This can lead to imbalances in body chemistry and hormones, affecting erectile function.
- Medications: Some drugs, including certain antihypertensives, antidepressants, and antipsychotics, can cause ED as a side effect.
- Substance Abuse: Alcoholism, smoking, and illicit drug use can damage blood vessels and reduce blood flow to the penis.
Psychological Causes
- Stress and Anxiety: These can interfere with the signals from the brain that start the erection process.
- Depression: It often lowers libido and can lead to ED.
- Performance Anxiety: Fear of sexual failure can create a self-fulfilling prophecy.
- Relationship Issues: Tensions and lack of communication with a partner can contribute to ED.
Symptoms of Erectile Dysfunction
The primary symptom of erectile dysfunction is the inability to get or keep an erection firm enough for sexual intercourse.
Other symptoms may include:
- Reduced sexual desire or libido
- Difficulty getting an erection
- Difficulty maintaining an erection during sexual activities
It’s important to note that occasional difficulty with erections is not necessarily a cause for concern. However, if the issue is persistent, it may be indicative of ED.

Diagnosing Erectile Dysfunction
Diagnosis involves a combination of physical examinations, medical history evaluation, and specialized tests.
Medical History : A thorough medical history helps identify any underlying conditions or risk factors. Patients are often asked about their
- Sexual history and the nature of the dysfunction
- Medical conditions and surgeries
- Medications and substances used
- Psychological state and stress levels
Physical Examination
A physical exam may involve:
- Examination of the penis and testicles to check for abnormalities
- Checking blood pressure and heart health
- A rectal exam to check the prostate
Laboratory Tests
Tests may be conducted to diagnose underlying conditions:
- Blood Tests: To check for diabetes, heart disease, and testosterone levels.
- Urinalysis: To look for signs of diabetes and other underlying health conditions.
- Ultrasound: To examine blood flow to the penis.
- Psychological Exam: To screen for depression and other psychological conditions.

Treatment Options for Erectile Dysfunction
Treatment depends on the underlying cause and can include lifestyle changes, medications, therapies, and surgical options.
Lifestyle Changes
- Exercise: Regular physical activity improves blood flow and cardiovascular health.
- Healthy Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can improve overall health and reduce ED risk.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can prevent and manage conditions like diabetes and hypertension that contribute to ED.
- Quitting Smoking: Smoking can damage blood vessels and restrict blood flow to the penis.
- Limiting Alcohol: Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to ED.
Medications
- Oral Medications: PDE5 inhibitors (sildenafil, tadalafil, vardenafil) increase blood flow to the penis.
- Hormone Therapy: Testosterone replacement therapy may be used if low testosterone levels are detected.
- Injections and Suppositories: Medications like alprostadil can be injected directly into the penis or inserted as a suppository into the urethra.
Devices and Surgery
- Vacuum Erection Devices: These devices create a vacuum that pulls blood into the penis.
- Penile Implants: Surgical implants can be semi-rigid or inflatable, allowing for an erection.
- Vascular Surgery: In cases of vascular blockages, surgery can improve blood flow to the penis.
Psychological Counseling
For cases where psychological factors play a significant role, counseling and therapy can be very effective. Techniques include:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Helps address negative thought patterns and behaviors.
- Sex Therapy: Focuses on resolving relationship issues and improving sexual communication and performance.
- Stress Reduction Techniques: Mindfulness, meditation, and other stress-reducing practices can also be beneficial.
Prevention of Erectile Dysfunction
While not all cases of ED are preventable, several strategies can reduce the risk:
- Regular Exercise: Keeps blood vessels healthy and improves circulation.
- Healthy Diet: Prevents conditions like diabetes and heart disease.
- Routine Health Check-Ups: Early detection and management of health conditions.
- Avoiding Substance Abuse: Reduces the risk of damage to blood vessels and nerves.
- Stress Management: Reduces psychological causes of ED.
- Healthy Sexual Relationships: Open communication with a partner can prevent performance anxiety and relationship-induced ED.
The Psychological Impact of Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction can have a profound impact on mental health and quality of life. It often leads to:
- Low Self-Esteem: Men may feel inadequate or embarrassed about their condition.
- Anxiety and Depression: Persistent ED can contribute to significant emotional distress.
- Relationship Strain: Can lead to misunderstandings and reduced intimacy in relationships.
- Coping Strategies for Erectile Dysfunction
- Open Communication: Discussing the condition with a partner can alleviate pressure and foster understanding.
- Seeking Professional Help: Professional counseling can provide support and coping mechanisms.
- Education: Understanding ED and its causes can reduce anxiety and empower men to seek appropriate treatment.
- Support Groups: Connecting with others who have similar experiences can provide emotional support and practical advice.

The Future of Erectile Dysfunction Treatment
Research continues to advance in the field of erectile dysfunction, with promising new treatments on the horizon:
- Stem Cell Therapy: Early studies suggest that stem cells could potentially regenerate erectile tissue.
- Gene Therapy: This approach aims to correct underlying genetic causes of ED.
- Novel Medications: New drugs targeting different pathways involved in erections are under investigation.
- Improved Devices: Advances in technology are leading to more effective and less invasive devices for managing ED.
Erectile dysfunction is a complex condition with a wide array of causes and treatments. It is a common issue that can affect men of all ages and backgrounds. Understanding the underlying factors, seeking appropriate treatment, and making lifestyle changes can significantly improve sexual health and overall well-being.
Open communication, both with healthcare providers and partners, is essential in managing and overcoming ED. With ongoing research and advancements in medical science, the future holds promising possibilities for even more effective treatments for erectile dysfunction.

